The Acadian flycatcher is a small flycatcher. It is around 5 inches (12.7 cm) in length.
It has greenish-brown upperparts, a grayish-white throat, a white lower breast, a light yellow belly, white wing bars, and white rings around its eyes. Males and females look alike.
The Acadian flycatcher is found in deciduous forests and by the sides of streams.
The Acadian flycatcher eats insects. It perches on a branch and waits for them to fly by. It then swoops after the insect and catches it in mid-air. It also gleans insects from foliage. It sometimes eats seeds and berries.
The female lays 2-4 eggs in an open cup nest woven of plant fibers and placed in a bush or tree, sometimes over a stream. The chicks hatch in two weeks and fledge when they are 13-15 days old. The female may have two broods a year.
The Acadian flycatcher has an average lifespan of 5 to 6 years in the wild. The oldest Acadian flycatcher on record lived to be 10 years and 11 months old.
The Acadian flycatcher is an excellent flyer and very good at maneuvering while in flight. It can hover and even fly backwards. It even flies when it is taking a bath. It dives into the water and then returns to its perch and shakes off the water and then preens.
Support for NatureWorks Redesign is provided by:


Though rare, the Acadian flycatcher is found in southern New Hampshire.
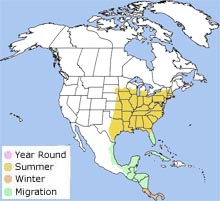
The Acadian flycatcher is a neotropical migrant. It breeds in the eastern half of the United States from Minnesota to southern New England and south to the Gulf Coast and Florida.
It winters in northwestern South America in lowland tropical forests in Colombia, Venezuela, and Ecuador.
NHPBS inspires one million Granite Staters each month with engaging and trusted local and national programs on-air, online, in classrooms and in communities.