The bobolink is a small songbird. It is between 6-8 inches (15–21 cm) in length and has a wingspan of around 10.5 inches (27 cm).
During the mating season, the male bobolink is black with a white back and a light yellow patch on the back of its head.
The female bobolink is yellowish brown with black stripes on her head and back.
After the mating season is over, the male molts and grows new feathers and looks like the female.
During the breeding season, the bobolink breeds in open grassland and hay fields. During migration and in the winter it can be found in freshwater marshes, grasslands, and rice fields.
The bobolink feeds on the ground, eating seeds, grains, insects, and spiders. Although it usually feeds during the day, during migration, the bobolink has been observed feeding in rice fields after dark on bright nights.
Scientists believe it eats at night during this time to build up fat stores for its long migration.
The bobolink uses grass and sedges to build a nest on the ground. Sometimes, it makes a canopy out of dead grass over the top of its nest for additional camouflage.
The female lays 1-7 bluish-gray eggs. She incubates them for 11-13 days. The chicks leave the nest after two weeks.
The bobolink has a lifespan of 4-6 years in the wild.
The bobolink is an incredible traveler. It makes a round-trip journey of about 12,500 miles (20,117 km) each year between North America and South America.
The bobolink is sometimes known as the rice bird.
Support for NatureWorks Redesign is provided by:


The bobolink is found throughout New Hampshire.
The bobolink population has been decreasing dramatically in New Hampshire due to the loss of farmland and grassland habitats.
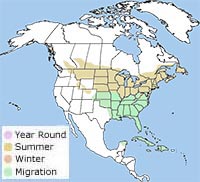
The bobolink breeds in the central and northeastern United States and southern Canada.
In the winter, it migrates to South America, settling in parts of Bolivia, Paraguay, Argentina, and Brazil.
During its long migration, it can be found throughout parts of South America, the Caribbean, and the southern United States.
NHPBS inspires one million Granite Staters each month with engaging and trusted local and national programs on-air, online, in classrooms and in communities.