The mink frog is 2-3 inches (5.1-7.6 cm) in length. It is olive green to brown and has dark blotches and spots on its body. It has creamy white to yellow undersides, and its lips are usually bright green.
It has a large tympanum on the sides of its head. The tympanum is a circular external eardrum.
The mink frog eats aquatic insects, snails, spiders, and other invertebrates. The mink frog tadpole eats algae and plant matter.
Breeding season runs from May through August. Males float in the water and call to the females. The female lays a mass of 500-4,000 eggs in deep water.
The male fertilizes the eggs after the female lays them. The tadpoles become frogs in about a year.
The mink frog is often found near lots of water lilies. The water lilies provide cover from predators and the lily pads are great platforms for the mink frog to hop around on.
The mink frog gets its name from the musky mink-like odor it produces when it is picked up or disturbed by a predator. Some people compare the smell to rotting onions.
Support for NatureWorks Redesign is provided by:


The mink frog is found in New Hampshire, north of the White Mountains. It is considered a species that is vulnerable to extirpation in the state.
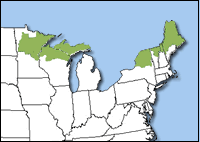
The mink frog is found in northern New England and New York and in Northern Minnesota, Michigan, and Wisconsin. It is also found in Canada from Nova Scotia west to Manitoba.
NHPBS inspires one million Granite Staters each month with engaging and trusted local and national programs on-air, online, in classrooms and in communities.