The boreal owl is a small owl. It is 8.3-11.0 inches (21-28 cm) in length and has a wingspan of 21.6-24.4 inches (55-62 cm).
It has no ear tufts, a small square head, and a white face outlined in black. Many people think the owl looks like it has a white “X” on its face.
It has a white body streaked with brown feathers, little white dots on its head, yellow eyes, and a yellow bill. Males and females look alike, but females are larger than males.
The boreal owl is found primarily in dense coniferous forests with spruce and balsam fir. It can also be found in deciduous forests with aspen, poplar, and birch trees.
In North America, the boreal owl is found at elevations from 5,200 to 10,500 feet (1,585-32,000 m).
The boreal owl is carnivorous and feeds on small mammals like voles, mice, chipmunks, and squirrels. It also eats insects and small birds, such as the American robin.
Hunting from a protected perch, the boreal owl swoops down and grabs its prey with its long talons. During winter and breeding season, the boreal owl caches, or saves, its food in its nest or in the crook of a tree.
Breeding season is from March to June. Depending on the amount of food available, the boreal owl will lay different numbers of eggs. Usually, the female lays 4-5 eggs. She incubates the eggs for 28 days.
The male hunts and brings food to the female, but otherwise stays away from the nest. Once the eggs hatch, the male brings food for the female and the chicks. Chicks fledge, or fly, about thirty days after hatching.
The boreal owl has a lifespan of 7-8 years in the wild. The oldest boreal owl on record lived to be 15 years and 11 months old.
The primary predators of the boreal owl are other owls and hawks, like the great horned owl and the Cooper’s hawk. When a boreal owl senses a predator, it tries to become very small and motionless, in hopes that the predator won’t see it.
The boreal owl is nocturnal and hunts at night.
Support for NatureWorks Redesign is provided by:


The boreal owl is a rare winter visitor to NH. It is sighted in the state every 3-5 years. There is a single breeding record for the owl from 2001.
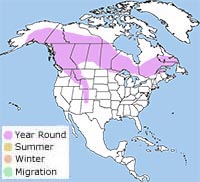
In North America, the boreal owl is found from Alaska to eastern Canada in subalpine and boreal forests. It is also found in the Cascade and Rocky Mountains and in the very northern part of Minnesota.
It sometimes visits northern states, including New Hampshire, in the wintertime.
The boreal owl is also found in Europe and Asia.
NHPBS inspires one million Granite Staters each month with engaging and trusted local and national programs on-air, online, in classrooms and in communities.