The brown bear has a slight hump above its shoulder, round ears, a long snout, and big paws with long, curved claws that it uses for digging. Unlike the black bear, it can’t climb trees.
It can weigh between 350-1,500 pounds(159-680 kg). When standing on its hind legs, it can be up to 5 feet (1.5 m) tall. Males are larger than females.
The brown bear is not always brown. It has fur that ranges from a cream or silver color to an almost black color.
The brown bear is also known as the grizzly bear. Some brown bears have fur that is tipped in a lighter color than the rest of their fur. This gives the fur a grizzled look and is how the bear got the name grizzly bear.
The brown bear is omnivorous. It eats berries, roots, fungi, grasses, fish, carrion, small mammals, and insects. It is very good at catching fish, and it often uses its long claws to dig insects out of rotting logs and small mammals out of their burrows. The brown bear usually forages for food in the early morning and evening and rests during the day.
Some brown bears in the Canadian Rockies hunt larger animals like moose, elk, and goats.
Mating season runs from May to early July. It takes from 180-266 days for cubs to be born. Cubs are usually born between January and March. The female usually has two cubs. The cubs are blind and furless and weigh around a pound (0.45 kg) when they are born.
The cubs are weaned when they are about five months old, but they usually remain with their mother for two to three years. Brown bear cubs can climb trees until they are about a year old.
The brown bear has a lifespan of 20-30 years in the wild.
The brown bear digs a den under rocks or in the hollow of a tree. It may also make its den in a cave or crevice. The brown bear goes into its den between October and December and stays there until the early spring. It has a protective layer of fat that allows it to stay in its den while the weather is cold. It does not really hibernate and can easily be woken up in the winter.
A brown bear’s home range can be between 70 and 400 square miles (113-644 km2). More than one bear may share the same home range, although they sometimes fight over a good fishing spot.
The brown bear is a threatened species in the lower 48 states. There are currently about 1,200 brown bears in the lower 48 states and about 31,700 brown bears in Alaska.
Support for NatureWorks Redesign is provided by:


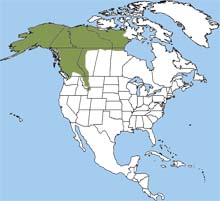
The brown bear’s range is circumpolar. That means it circles the Arctic. It is found from the Arctic coast down into central parts of Europe and Asia. In North America, it is found in Alaska, with small populations in Wyoming, Montana, Idaho, and Washington as well as western Canada.
The brown bear was once common west of the Mississippi, but its population dropped as the west was settled.
NHPBS inspires one million Granite Staters each month with engaging and trusted local and national programs on-air, online, in classrooms and in communities.