The margay is about 2 feet (0.61 m) tall from feet to shoulders, 3 feet long (0.9 m) from nose to tail tip, and it weighs about 5-12 pounds (2.3-5.4 kg).
It has gray to golden-brown fur with black and brown spots. The spots on its sides are often different shapes and are often black with a brown center. Its underside is white. The margay has a small head, large ears and eyes, and a long tail.
The margay makes its home in tropical and subtropical forests.
The margay eats a wide variety of food including birds, bird eggs, small mammals, reptiles, and fruit. It hunts primarily in trees.
Margays mate year-round. Females give birth to one or two young, three to four months after mating. The kittens begin to eat meat when they are about eight weeks old.
The margay has a lifespan of 12-14 years in the wild and 20-25 years in captivity.
The margay is nocturnal. It is an excellent climber and jumper. It has joints in its ankles that rotate 180 degrees. This helps it climb down vertical trees headfirst. It is the only cat in North America that can do that. It can also hang from tree limbs by one hind foot.
It spends most of its time in the tree canopy hunting for birds, small mammals, reptiles, and eggs.
Support for NatureWorks Redesign is provided by:


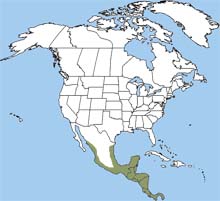
The margay is found from Mexico to Argentina. It was once found in the United States in Texas. The last margay seen in the United States was spotted in Texas in the 1850s.
NHPBS inspires one million Granite Staters each month with engaging and trusted local and national programs on-air, online, in classrooms and in communities.