The red fox has orangish-red fur on its back, sides, and head. It has white fur under its neck and on its chest. It has a long bushy tail tipped in white, pointed black ears, and black legs and feet.
The red fox is the size of a small dog. They are 3-3.5 feet (0.91-1 m) in length, including their tails, which are 14–16 inches (35-43 cm) long. They stand 15-16 inches (38-41 cm) at the shoulder. They weigh 8-15 pounds (3.6-6.8 kg). Males are larger than females.
The red fox makes its home in wooded areas, prairies, and farmland.
The red fox eats a wide variety of foods. It is an omnivore, and its diet includes fruits, berries, and grasses. It also eats birds and small mammals like squirrels, rabbits, and mice. A large part of the red fox’s diet is made up of invertebrates like crickets, caterpillars, grasshoppers, beetles, and crayfish.
The red fox will continue to hunt even when it is full. It stores extra food under leaves, snow, or dirt.
The red fox mates from January through March. The female makes one or more dens right after mating. The extra dens are used if the original den is disturbed. A little less than two months after mating, the female gives birth to a litter of between one and ten kits. The male brings the female food while she is caring for the kits.
The kits start playing outside the den when they are about a month old. The mother begins feeding her kits regurgitated food, but eventually, she will bring them live prey to “play” with and eat. Playing with live prey helps the young kits develop the skills they will need for hunting. The kits leave their mother when they are about seven months old.
The red fox has a lifespan of 3 to 5 years in the wild. They can live to be 15 years old in captivity. In the wild, their lifespan can be shortened by predation, hunting and trapping, and competition for resources.
The red fox is mostly nocturnal, although it sometimes ventures out during the day. Unlike many other mammals, the red fox can hear low-frequency sounds very well. It can hear small animals digging underground and frequently digs in the dirt or snow to catch prey.
The red fox stalks its prey much like a cat, getting as close as possible before pouncing and giving chase.
Except for breeding females, the red fox does not usually use a den. Sometimes it sleeps in the open, wrapping its bushy tail around its nose to stay warm. When it does use a den, it usually finds an abandoned rabbit or marmot burrow rather than digging its own.
Support for NatureWorks Redesign is provided by:


The red fox is found throughout New Hampshire.
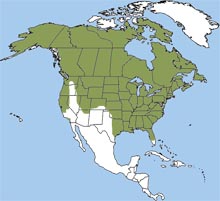
The red fox is found in most of the United States and Canada, except for the far north in Canada and Alaska, and much of the western U.S. and Hawaii.
The red fox is also found in Europe and Asia, and it has been introduced to Australia.
NHPBS inspires one million Granite Staters each month with engaging and trusted local and national programs on-air, online, in classrooms and in communities.